Mali Empire: gold, kings, and scholars of Timbuktu
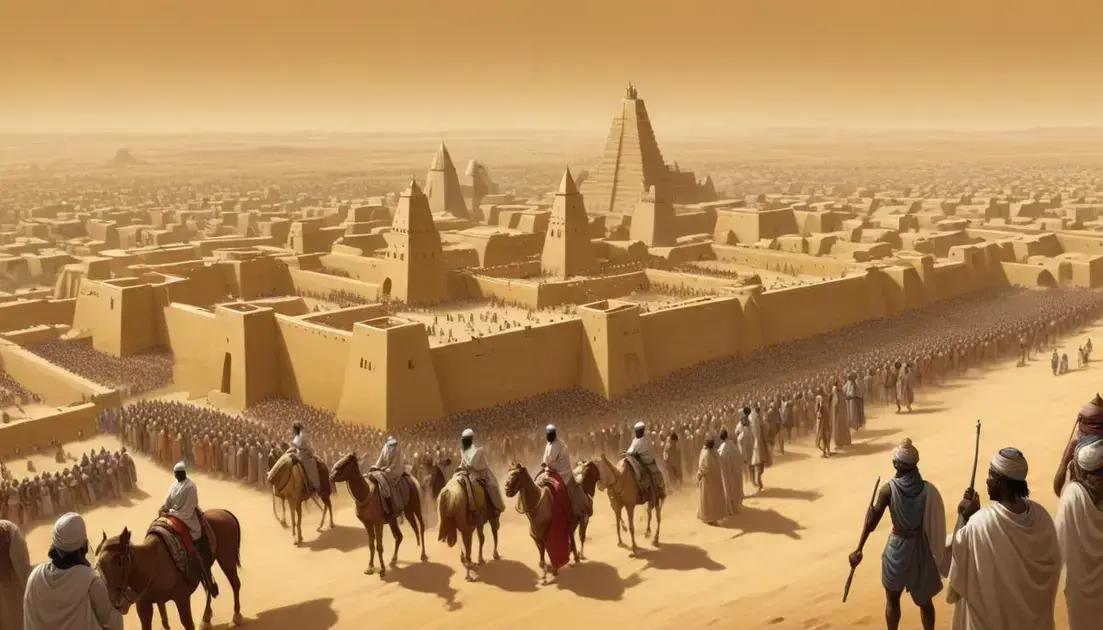
The Mali Empire was a powerful West African civilization known for its wealth, education, and cultural contributions. Famous ruler Mansa Musa expanded its influence through trade, particularly in gold. Timbuktu emerged as a significant center of learning and culture during this period. The empire’s architectural advancements and rich history continue to impact modern West Africa, highlighting the importance of education and cultural exchange.
Welcome to the world of the Mali Empire, where wealth and wisdom flourished in West Africa. Have you ever wondered how this great empire influenced the culture and history of the region? Let’s dive in!
The Rise of the Mali Empire
The rise of the Mali Empire is a fascinating story of growth and strength. It began in the 13th century, when legend says a man named Sundiata Keita united several tribes. His bravery and vision laid the foundation for what would become one of the greatest empires in West Africa.
With fertile land, cities like Niani grew as trade hubs. They connected the salt and gold routes, bringing in wealth and influence. Merchants traveled far and wide to engage in trade, making Mali a key player in the region.
Leadership and Expansion
Under Sundiata’s leadership, Mali expanded significantly. After him, the empire was led by powerful kings, or ‘Mansas’. Each contributed to Mali’s growth. Mansa Musa, the most famous, is known for his pilgrimage to Mecca. He brought back ideas, education, and culture that enriched the empire.
Cultural Flourishing
The rise of the Mali Empire was not just about wealth. It was a time of cultural flourishing. The empire attracted scholars from all around. Timbuktu developed into a center of learning. Libraries and universities were established, making knowledge accessible to many.
The empires’ influence spread beyond trade and wealth. They had a strong impact on art, music, and architecture. The buildings from this era often blended local styles with Islamic influences, creating a unique cultural heritage.
Mansa Musa: The Richest King
Mansa Musa was an extraordinary ruler of the Mali Empire. Known as the richest king in history, he ruled from 1312 to 1337. His wealth mainly came from the abundant gold mines in Mali. But Mansa Musa was more than just rich; he was also wise and generous.
His famous pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324 attracted global attention. He traveled with a caravan of thousands, carrying gold and gifts. Along the way, he shared his wealth with everyone he met. Cities like Cairo felt his impact as he spent gold, making prices rise.
Impact on Culture
Mansa Musa loved learning and culture. He built schools and mosques in cities like Timbuktu. These places became centers of knowledge and religion. Scholars from different regions came to study and teach there.
Legacy of Wealth
His wealth opened doors for trade. The Mali Empire thrived under his rule. Traders flocked to Mali, eager to buy gold and other goods. Mansa Musa’s connection to trade made Mali a powerful empire in Africa.
Even today, his name represents wealth and generosity. Mansa Musa’s story teaches us about the importance of using riches wisely and sharing with others.
Timbuktu: A Center of Learning and Culture
Timbuktu is known as a center of learning and culture in the Mali Empire. This city became famous for its rich history and education. In the 14th century, it flourished as a gathering place for scholars and students. People traveled great distances to learn and share knowledge.
One of the notable institutions was the Sankore University. It was a place for advanced studies in various subjects. Scholars taught subjects like mathematics, astronomy, and Islamic studies. The university attracted brilliant minds from across the region.
Libraries and Manuscripts
Timbuktu was home to many libraries filled with valuable manuscripts. These texts contained ancient knowledge and ideas. They are treasured historical resources today. People studied philosophy, medicine, and poetry in these libraries.
Cultural Impact
The cultural impact of Timbuktu is still evident today. The city was a melting pot of ideas, languages, and traditions. Artists and musicians also thrived, contributing to the vibrant culture. This rich tapestry of life laid the foundation for future generations.
Even though Timbuktu faced challenges over the years, it remains a symbol of knowledge and cultural heritage. Many still admire its legacy as a great center for education.
Trade and Wealth: How Gold Shaped the Empire
Gold played a vital role in shaping the Mali Empire. It was one of the empire’s main resources. The abundant gold mines brought incredible wealth to Mali. Traders came from far and wide to exchange goods.
The empire controlled crucial trade routes across West Africa. This control allowed the Mali Empire to prosper. Merchants traded gold for other valuable items like salt, ivory, and textiles. As trade expanded, so did the empire’s influence.
Economic Growth
Wealth from gold mining led to economic growth. Mansa Musa used his riches to build cities and improve infrastructure. He constructed roads, bridges, and mosques, making trade even easier. This development attracted more merchants and travelers.
Impact on Society
The wealth also helped improve society. Education and culture flourished as a result. Wealthy patrons funded schools and scholars. As Timbuktu grew, it became a hub for learning and culture.
Additionally, gold provided power. The Mali Empire became a dominant force in the region. With power came respect from neighboring states. This established Mali as an empire to be reckoned with.
The Legacy of the Mali Empire
The legacy of the Mali Empire is rich and profound. It left lasting impacts on culture, education, and trade. Even after its decline, its influences can still be seen today. This empire set the stage for future generations in West Africa.
One of the greatest contributions was the spread of education. Timbuktu became a center for learning. Scholars from various backgrounds came to study. This exchange of knowledge enriched many cultures and laid foundations for future academic pursuits.
Architectural Contributions
The Mali Empire also made significant contributions to architecture. The famous mud mosques and buildings still stand today. They showcase the unique architectural styles that blend local and Islamic influences.
Influence on Trade
The empire influenced trade routes across West Africa. As traders exchanged goods, they shared ideas and cultures too. This interaction helped shape the diverse cultures present in the region today.
Mali’s legacy lives on through its rich history, culture, and contributions to education. The story of this empire is a reminder of the importance of knowledge and cultural exchange.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Mali Empire left a remarkable legacy that still resonates today. Its contributions to education, architecture, and trade shaped the culture of West Africa. The advancements in learning and the cultural exchanges created a rich environment for future generations.
The buildings and mosques that stand today remind us of the empire’s architectural brilliance. This history teaches us the value of knowledge and sharing ideas with others. As we reflect on the legacy of the Mali Empire, we see how important it is to foster education, culture, and trade for a brighter future.